A 205 million year-old bone discovered in the UK belonged to a sea reptile approaching the size of a blue whale, according to experts.
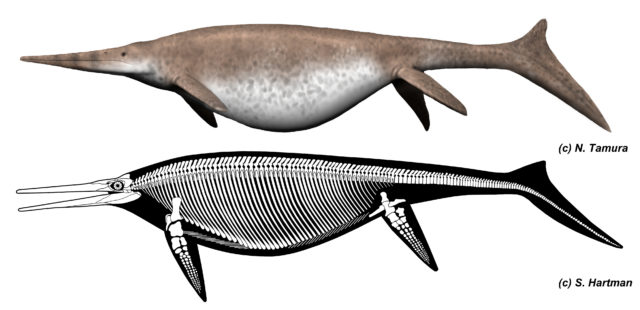
The jaw bone, found on the beach at Lilstock in Somerset, has been identified as that of a giant ichthyosaur.
The largest reported ichthyosaurs – the shastasaurid – lived during the late Triassic period, around 200 to 235 million years ago, and ranged from 6m to more than 20m long.
Paul de la Salle, a fossil collector and co-author of the study, discovered the jaw bone in May 2016.
“Initially the bone just looked like a piece of rock but, after recognising a groove and bone structure, I thought it might be part of a jaw from an ichthyosaur,” he said.
He later returned and found more pieces measuring around one metre in length.
The specimen was identified as an incomplete bone, known as a surangular, from the lower jaw of an ichthyosaur by experts Dean Lomax, of the University of Manchester, and Professor Judy Massare of Brockport College, New York.

Mr Lomax said: “As the specimen is represented only by a large piece of jaw, it is difficult to provide a size estimate, but by using a simple scaling factor and comparing the same bone in Shonisaurus sikanniensis, the Lilstock specimen is about 25% larger.
“Other comparisons suggest the Lilstock ichthyosaur was at least 20 to 25 metres.
“Of course, such estimates are not entirely realistic because of differences between species.
“Nonetheless, simple scaling is commonly used to estimate size, especially when comparative material is scarce.”
They were previously thought to belong to dinosaurs but the authors said they could also be from a giant ichthyosaur, even bigger than the specimen found in Lilstock.
Mr Lomax said: “One of the Aust bones might also be an ichthyosaur surangular.
“If it is, by comparison with the Lilstock specimen, it might represent a much larger animal.
“To verify these findings, we need a complete giant Triassic ichthyosaur from the UK – a lot easier said than done.”






