Water flowing from mountains to fjords in Norway will soon be helping power British homes, as the world’s longest “interconnector” hooks up the two countries’ grids.
The 447-mile (720km) cable being laid between the UK and Norwayis one of a series of grid connections with other countries that will help reduce carbon emissions from the British power sector by 17% by 2030, National Grid said.
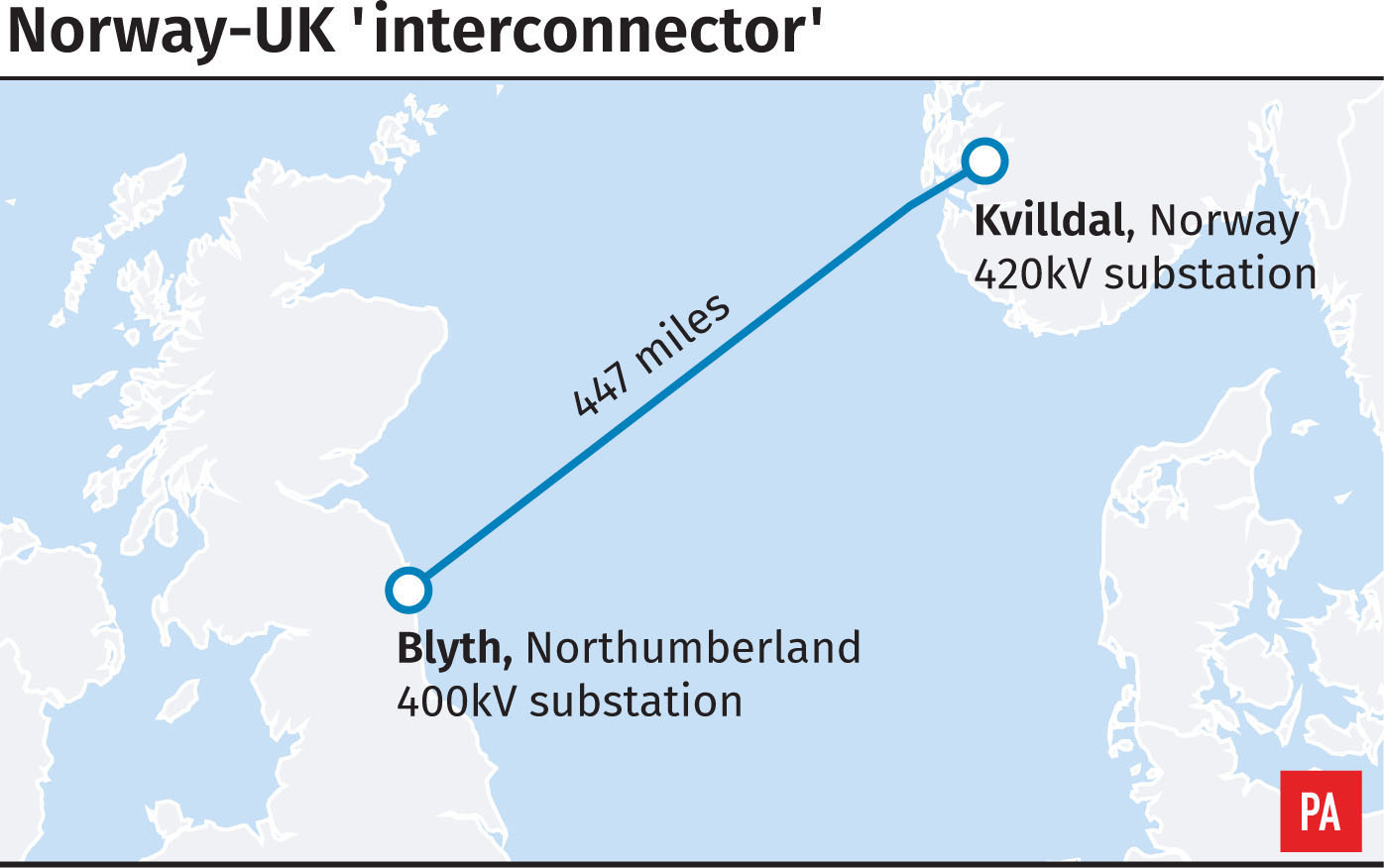
They will carry the renewable power under the sea to another converter station at Blyth, Northumberland, where it will enter the British grid.
The 6in (15cm) wide cables will be able to transmit 1,400 megawatts of electricity – enough to meet the peak winter power demand of three cities the size of Newcastle, according to project director Nigel Williams, from National Grid.
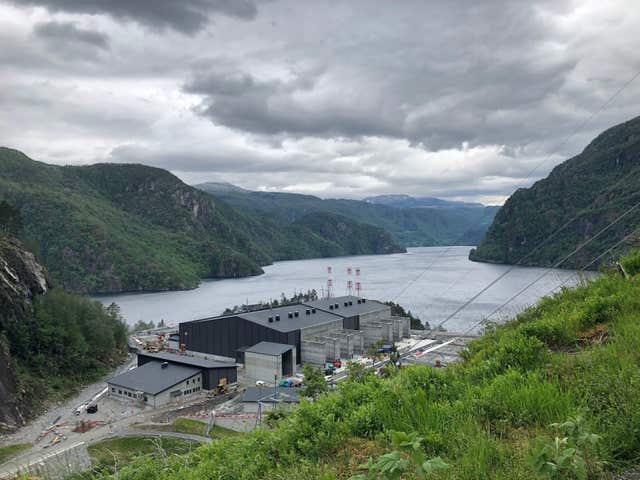

The reservoir, constructed with a series of dams high up in mountains capped with snow and lakes, stores water from rainfall and snow melt as part of a vast hydropower network with a 770 square mile (2,000 sq km) catchment.
When power is needed, water is released from the reservoir through pipes to hydropower plants, generating electricity by turning turbines as it flows down towards the lake and fjord below.
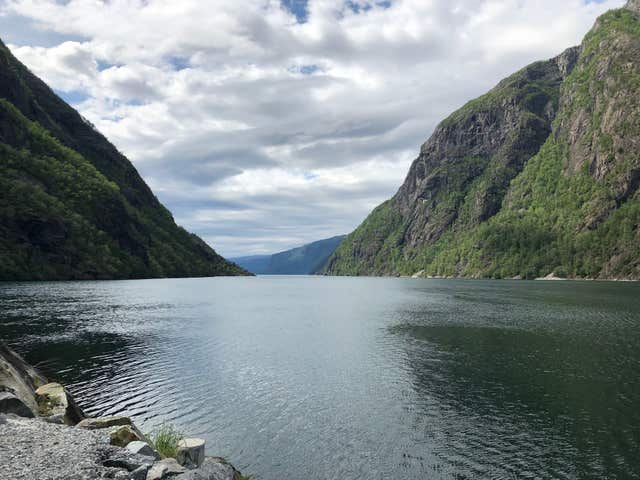

But as more offshore wind farms are built in the UK, there will be times the British grid has more renewable power than it needs, and it will be able to transmit electricity to power homes in Norway.
This will mean the Norwegian grid can effectively store energy by holding back the water in the reservoir for use in the hydropower plants at another time.
It could even use the excess electricity to pump water back up from lower levels into the reservoir for future use, allowing both countries to make the best use of their renewable resources, the team behind the scheme say.
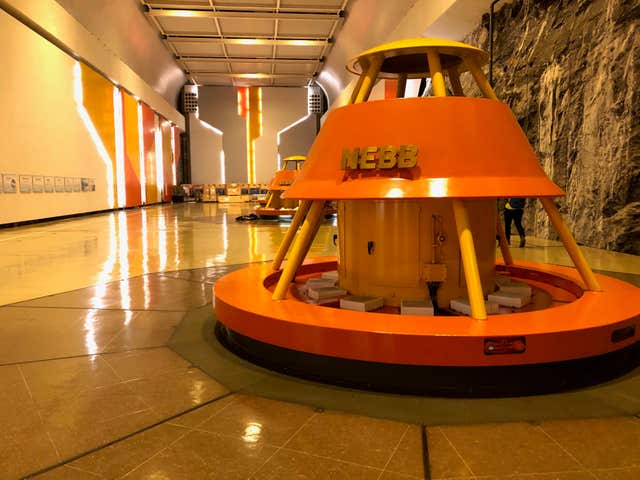

“Norway presents a great opportunity to get some of their excess hydro over to the UK which will displace some of the fossil fuel plant.”
And he said hydro is cheap.
“It reduces customer bills in the UK because we will be replacing top-of-the-range coal and gas plant with baseload hydro, so energy prices will have a downward effect in the UK.”
River levels affected by the hydro scheme are managed to protect nature, including wild salmon returning to spawn, and the engineers laying the interconnector cables through the lake had to protect the trout living there.
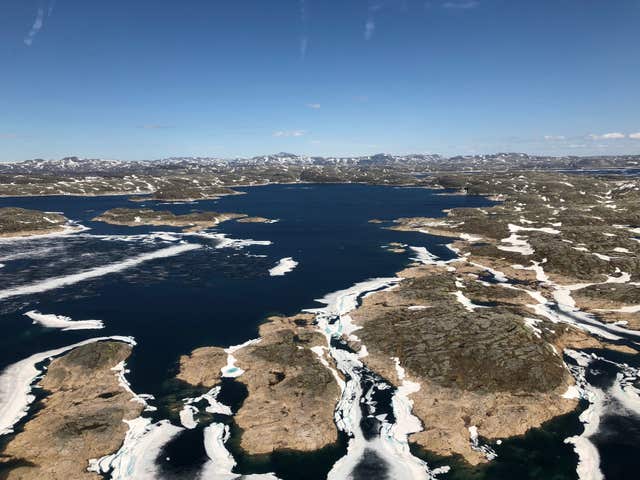

It also addresses the charge against renewables that when the wind does not blow or the sun does not shine, gas or coal are needed, as it provides clean power from Norway.
“All of this is helping us to decarbonise our power system which is absolutely crucial to the kind of action we need to take to tackle the climate crisis,” he said.






